Did you know that iodine deficiency is a leading cause of thyroid disease? But what is iodine and where do you get?
Also, what’s thyroid disease?
May marks thyroid awareness month, and as such, we’ve called on our experts to help put this important information together.
We find out and explain
- What the thyroid gland is and its functions
- The deal with iodine
- Iodine deficiency and thyroid disease
- Early detection of thyroid problems
- Preventing iodine deficiency
- Treating thyroid problems
The thyroid gland explained
Located in your neck, the thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development.
The hormones that the thyroid gland produces play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, the process by which the body converts food into energy.
They help regulate heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels.
The thyroid gland also produces a hormone called calcitonin, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
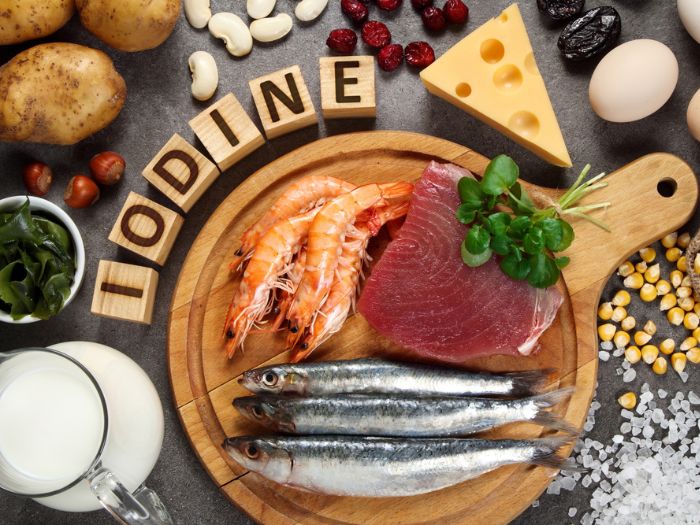
The deal with iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that’s important for health. It plays a key role in the functioning of the thyroid gland and is also important for the development of the brain and nervous system in infants and young children.
Our bodies need iodine to make thyroid hormones which are important for a large number of functions.
These thyroid hormones are especially important for proper bone and brain development during pregnancy and infancy.
We get iodine mainly from what we eat. These are some foods that are high in iodine:
- Seaweed and fish
- Dairy products
- Iodized salt
- Eggs
- Beef liver
- Chicken
If you don’t get enough iodine…
An iodine deficiency can lead to goitre (enlarged thyroid gland), hypothyroidism, and other health problems.
Signs of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue, lethargy
- Weakness
- Sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Weight gain
The World Health Organisation estimates that 2 billion people worldwide have insufficient iodine intake, making it a significant public health issue.
If you’re concerned about your iodine levels or experience any of the symptoms listed above, get in touch with our team of health professionals today.
Iodine deficiency is one of the leading causes of thyroid disease
Iodine deficiency is a leading cause of thyroid disease, so getting enough iodine through a balanced diet is essential.
Thyroid disease refers to any condition that affects the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Sadly, thyroid disease is a common disorder that affects millions of people worldwide and can have a significant impact on overall health, including:
- Weight gain or loss
- Fatigue
- Depression/psychological problems
- Anxiety
- Tremors
- Muscle weakness
- Cardiovascular disease
When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, there are two common outcomes:
- Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid)
- Hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid)
These conditions often lead to autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
The bottomline is: ensure you’re in good health and ensure you’re eating a balanced diet.
Early detection of thyroid problems
The early signs of thyroid problems can be subtle and can even go unnoticed, but there are several warning signs that may indicate an issue.
Fatigue, weight gain, and depression are common symptoms of hypothyroidism, while hyperthyroidism may cause anxiety, weight loss, and tremors.
Other symptoms of thyroid problems include hair loss, changes in heart rate, and sensitivity to cold or heat.
Blood tests and regular checkups can help detect thyroid dysfunction before symptoms appear.
Imaging tests such as ultrasounds can also provide valuable information about the size and function of the thyroid gland.
Preventing iodine deficiency
Preventing iodine deficiency is crucial for maintaining thyroid health. The recommended daily intake of iodine for adults is 150 micrograms and 220 mcg for pregnant women.
So, what does 150 micrograms mean?
Here’s a rundown of some foods and their iodine content (micrograms of iodine per 100 grams of food):
- Canned salmon: 60 mcg
- Bread (except organic bread): 46 mcg
- Regular milk: 23 mcg
- Eggs: 22 mcg
- Canned tuna: 10 mcg
Source: Food Standards Australia and New Zealand
Iodine requirements vary depending on age, gender, and pregnancy status, but in general, consuming iodine-rich foods is one of the best ways to prevent iodine deficiency.
Treating thyroid problems
Treatment for thyroid disease depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
For iodine deficiency-related hypothyroidism, treatment typically involves iodine supplements and thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, may be treated with medication to suppress the production of thyroid hormone or with radioactive iodine therapy to destroy overactive thyroid cells.
In some cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Goitres may be monitored or treated with medication, while thyroid cancer can require surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Alongside medical treatment, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise may help manage thyroid disease.
Iodine and thyroid disease in summary
Preventing iodine deficiency through diet and possibly supplements is essential for maintaining thyroid health, especially for pregnant and breastfeeding women, and young children.
Early detection is also a powerful weapon against preventing long-term health complications.
But knowing your thyroid health can be difficult to gauge.
If you experience any of the above conditions associated with thyroid problems, or simply haven’t had a checkup in a while, get in touch with our team today.